Litecoin (LTC) Analysis
In addition to automated chart patterns, altFINS’ analysts conduct technical chart analyses of top 30 cryptocurrencies. We call these Curated Charts and they evaluate 5 core principals of technical analysis: Trend, Momentum, Patterns, Volume, Support and Resistance.
Litecoin (LTC) Trends
Litecoin (LTC) Performance
Litecoin (LTC) RSI & MACD
Litecoin (LTC) technical analysis:
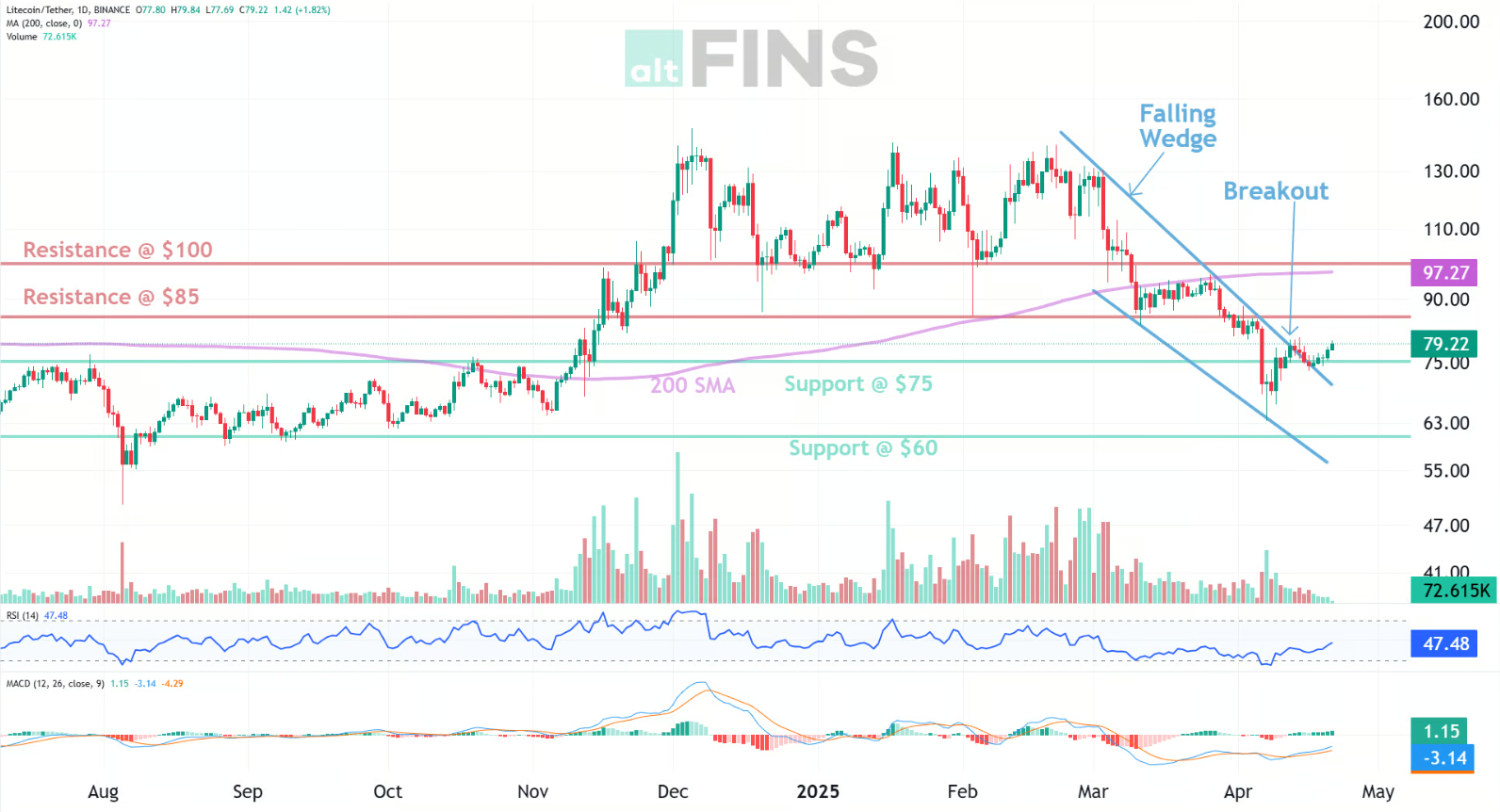
Trade setup: Price is in a Downtrend, however, it had a bullish breakout from Falling Wedge pattern, which could signal at least a temporary bullish trend reversal with +15% upside potential to $85 resistance. Stop Loss at $68. This is a riskier trade setup because it’s a trend reversal not a trend continuation setup. It’s against the overall downtrend. On the positive note, this asset is likely to see a Spot ETF launched in 2025. (Set a price alert) Learn to trade Pullback in Uptrend strategy in Lesson 3 and Risk Management in Lesson 9.
Patterns: Falling Wedge usually results in a bullish breakout. When price breaks the upper trend line the price is expected to trend higher. Emerging patterns (before a breakout occurs) can be traded by swing traders between the convergence lines; however, most traders should wait for a completed pattern with a breakout and then place a BUY order. Learn to trade chart patterns in Lesson 8.
Trend: Short-term trend is Down, Medium-term trend is Strong Down, Long-term trend is Strong Down.
Momentum: Price is neither overbought nor oversold currently, based on RSI-14 levels (RSI > 30 and RSI < 70).
Support and Resistance: Nearest Support Zone is $75.00, then $60.00. Nearest Resistance Zone is $85.00, then $100.00.
See live Litecoin (LTC) chart here.
See more curated charts for top 65 coins.
Recent news and research:
- Litecoin Outpaces Dogecoin and Cardano in This Important Metric. Read more.
- Long-Term Litecoin (LTC) Holders Count Hits 5 Million. Read more.
- XRP Volume Rises to $720 Million: Surpasses Dogecoin, Solana. Read more.
- Another major exchange has decided to list XRP but this time for trading against the EUR. Read more.
Find more real-time news here.
What is Litecoin (LTC)?
Find full description and news on altFINS platform.
Overview
Litecoin is a fork of Bitcoin’s codebase with four times faster block times and a four times larger supply. The project considers itself complementary to Bitcoin as a silver to Bitcoin’s gold. It is often used as a pseduo-testnet for Bitcoin, adopting new protocol changes before they are deployed on Bitcoin.
History
Created in October 2011 by ex Google and Coinbase engineer, Charlie Lee, Litecoin is a fork of Bitcoin’s source code that posits itself as “a silver to Bitcoin’s gold.” Technically, Litecoin is nearly identical to Bitcoin with key differences relating to block time, supply, hashing algorithm, and initial distribution. Litecoin aimed to keep the best aspects of Bitcoin while making some optimizations for its use as a medium of exchange. Notably, Litecoin implements 2.5 minute block times and an 84 million max supply. Charlie Lee’s original thinking was that quicker block confirmations would increase transaction throughput and reduce the amount of time merchants would need for block confirmations. Additionally, he thought the 84 million max supply would prevent the coin from becoming too scarce and expensive. Litecoin uses Scrypt, a memory intensive hashing algorithm, in order to better allow individuals to mine Litecoin with commodity hardware (although ASICs have been developed for Litecoin mining over the past few years). Finally, Charlie Lee, recognizing the mistakes of the few altcoins launched prior to Litecoin, wanted Litecoin to be launched in a fair manner, electing to only do a 150 coin (3 block) premine to allow people to get in early. Charlie Lee left Coinbase in June 2017 to head the Litecoin foundation, which stewards the Litecoin project, and finances Litecoin Core development.
Supply Curve Details
Litecoin was created as a clone of Bitcoin meant to have four times the supply, as well as generate blocks four times as fast. Bitcoin’s parameters were changed in order to achieve this, with the result that eventual supply will top out at no more than 84 million coins. On average, Litecoin generates new blocks every 2.5 minutes, rewarding miners with 12.5 new LTC and the total transaction fees from the preceding block. Each block has a 1MB limit and block rewards are halved every 840,000 blocks (approximately 4 years). Litecoin‘s first halvings occurred on August 2015 and August 2019. The next halving will occur in August 2023. Eventually, once the 84 million LTC hard cap has been reached, block rewards will transition entirely to transaction fees shifting the security model of the protocol to one based on demand for block space versus one based on demand for LTC. Similar to bitcoin, litecoin’s supply dynamics are known with great precision, and the vast majority of all eventual coins will be minted in the first two decades.
Consensus Details
Consensus Litecoin uses Nakamoto Consensus whereby the valid chain is the longest chain with the most accumulated proof-of-work. Consensus in Litecoin, and other systems using Nakamoto Conensus, is probabilistic because there is always a chance that a new, longer competing chain could emerge with more accumulated proof-of-work, that would invalidate the current chain. Mining Miners solve computational puzzles to generate new blocks using a Scypt algorithm. In this process, miners compete to generate a hash less than the target number set by Litecoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm. Similar to Bitcoin, the target difficulty level is adjusted every 2016 blocks; however, due to Litecoin’s 2.5 minute block times, Litecoin‘s difficulty level adjusts more quickly than Bitcoin’s. Litecoin originally implemented the Scrypt algorithm for its memory intensive properties, which made it more resistant to ASICs; however, over time Litecoin’s ASIC resistant properties have eroded with Scrypt-capable ASICs having been developed. Furthermore, in order to smooth individual miner revenue as mining has become more competitive, mining is now done in pools where participants contribute hash power to the pool and receive a proportional share of the profits if the pool finds a valid block.
Regulation
The Securities Framework Asset Ratings of the Crypto Rating Council (CRC) attributed the score of 1 out of 5 to Litecoin and provided the below summary: Absence of a marketed token sale and corresponding marketing efforts Decentralized development and usage The CRC is a member-owned and operated organization whose purpose is to assess if a crypto asset, or its development, issuance, and use have characteristics that make it more or less likely to implicate federal securities laws. According to the CRC framework, a score of 5 results when an asset appears to have many characteristics that are consistent with the Howey-test factors. A score of 1 results when an asset appears to have few characteristics that are consistent with the Howey-test factors.
Usage Details
LTC is used as a native currency within the Litecoin network. LTC can be used for peer-to-peer payments and value storage within the Litecoin network. With its faster block times, Litecoin aims to offer higher on-chain throughout and quicker confirmation times than Bitcoin. However, similar to Bitcoin, Litecoin plans to ultimately scale using layer 2 solutions such as the lightning network.
Launch Details
Litecoin initiated a 150 coin pre-mine, coins rewarded for mining the genesis block and 2 subsequent blocks, which were initially reserved for project development bounties. Its genesis block was on 10/7/2011.
Technology
Litecoin, the protocol, is a distributed, time-stamped ledger of unspent transaction output (UTXO) transfers stored in an append-only chain of 1MB data blocks. A network of mining and economic nodes maintains this blockchain by validating, propagating, and competing to include pending transactions (mempool) in new blocks. Economic nodes (aka “full nodes”) receive transactions from other network participants, validate them against network consensus rules and double-spend vectors, and propagate the transactions to other full nodes that also validate and propagate. Valid transactions are sent to the network’s mempool waiting for mining nodes to confirm them via inclusion in the next block. Mining nodes work to empty the mempool usually in a highest-to-lowest fee order by picking transactions to include in the next block and racing against each other to generate a hash less than the target number set by Litecoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm. Litecoin uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to establish the chain of blocks with the most accumulated “work” (a.k.a., energy spent on solved hashes) as the valid chain. Other network peers can cheaply verify the chain’s work.
Governance
Litecoin developement is open to the open source community. Protocol development is governed by a proposal process whereby anyone in the open source Litecoin community can submit Litecoin Improvement Proposals (“LIPs”). After debate by the community, the Litecoin Core editors, whom are supported by the Litecoin foundation, accept or reject the proposals. Decisions from the process are written into the Litecoin specification, as well as the software that runs the network. Finally, protocol changes are “ratified” on-chain when the majority of the network adopts the upgrade and doesn’t break consensus. Although Litecoin Core and the Litecoin Foundation are separate, they work closely together on the Litecoin project with the Litecoin Foundation providing funding to Litecoin core developers.
About altFINS
altFINS is the best crypto analytics platform. The platform will help you find the right crypto trading opportunities. You can search for coin in Uptrend, with Momentum or Breakouts. It’s is great for advanced traders but also for beginners to learn basics of technical analysis in Crypto trading Course or in Curated charts or Chart pattern sections. But also more advanced traders can create their own Screens and Alerts of coins with different trading strategies.