Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) Analysis
In addition to automated chart patterns, altFINS’ analysts conduct technical chart analyses of top 30 cryptocurrencies. We call these Curated Charts and they evaluate 5 core principals of technical analysis: Trend, Momentum, Patterns, Volume, Support and Resistance.
Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) technical analysis:
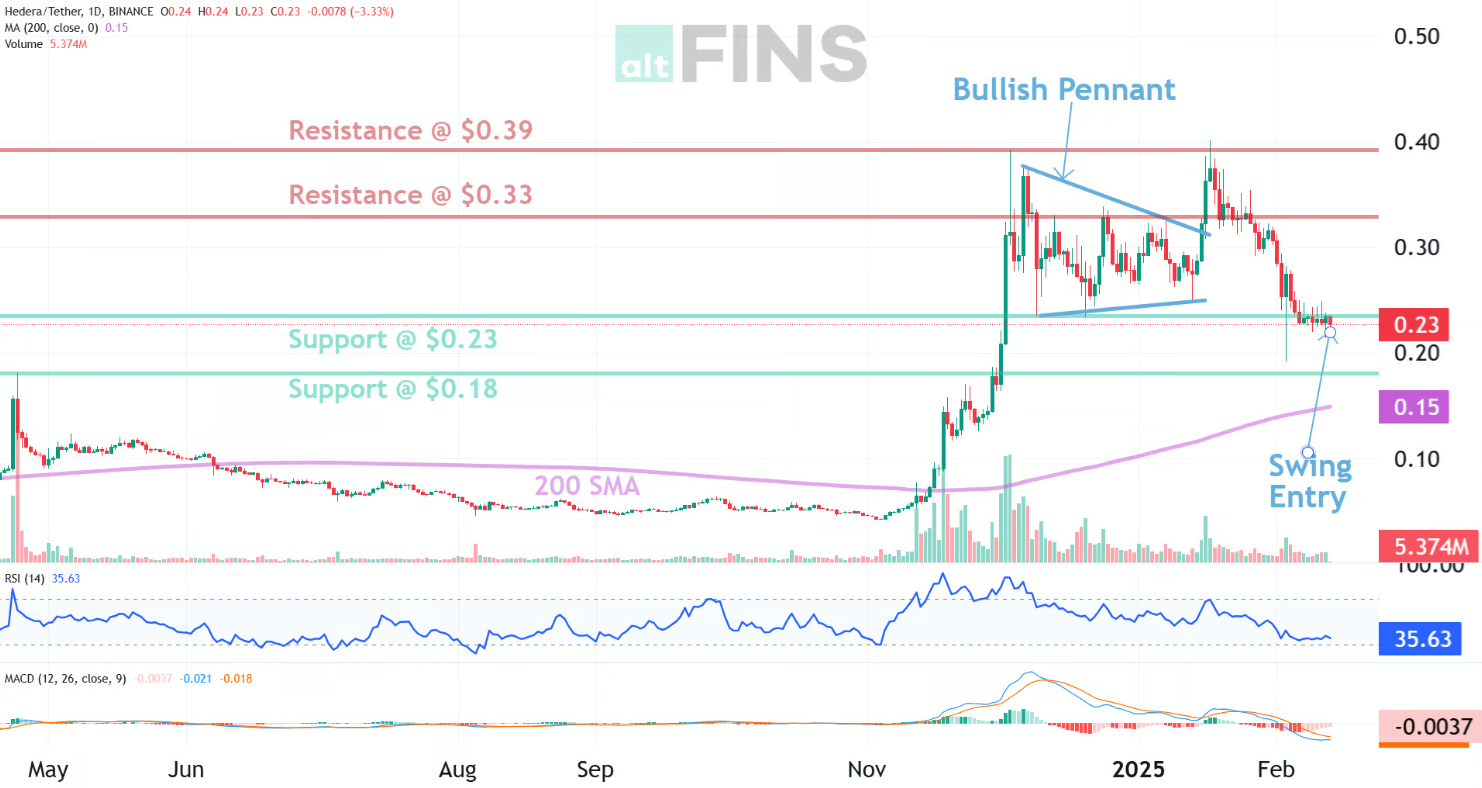
Trade setup: Price broke out of a Bullish Pennant pattern and reached $0.39 resistance again, where it got rejected 2x already. Pullback to $0.23 support is a swing trade entry opportunity in Uptrend, with +30% upside potential to $0.30 (PT1) or $0.39 (PT2). Stop Loss at $0.21. News of an ETF filling for HBAR was the trigger for the recent rally. (set a price alert). Learn how to use Fibonacci Retracement levels (possible support). Learn to trade breakouts in Lesson 7 and Risk Management in Lesson 9.
Pattern: Price is Approaching Support, which is a level where it could pause or reverse its recent decline, at least temporarily. Support is often a level where price has bounced up in the past, or potentially prior Resistance level that was broken. (concept known as polarity). Once price breaks below support, it can move lower to the next support level. Learn to trade key levels in Lesson 7.
Trend: Short-term trend is Down, Medium-term trend is Down, Long-term trend is Strong Up.
Momentum is Bearish but inflecting. MACD Line is still below MACD Signal Line but momentum may have bottomed since MACD Histogram bars are rising, which suggests that momentum could be nearing an upswing. Price is neither overbought nor oversold currently, based on RSI-14 levels (RSI > 30 and RSI < 70).
Support and Resistance: Nearest Support Zone is $0.18, then $0.14. Nearest Resistance Zone is $0.33, then $0.39.
See live Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR) chart here
See more curated charts of coins with technical analyses.
Recent news and research:
Solana And Hedera Holders Pivot To New Competitor Set To Rise From $0.05 To $5 By June. Read more.
Bill Morgan Predicts XRP and HBAR Will Surpass Major Cryptocurrencies by 2025. Read more.
Swiss-Based Hashgraph Group Secures License to Launch $100M Web3 Fund. Read more.
Find more real-time news here.
What is Hedera Hashgraph (HBAR)?
HBAR the native cryptocurrency of the Hedera Hashgraph network, is a powerful digital asset driving one of the most advanced distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) in the blockchain space. Built on the revolutionary Hashgraph consensus algorithm, Hedera offers unmatched speed, security, and scalability, making HBAR an ideal choice for enterprises, developers, and investors.
🪙 HBAR Token Utility and Use Cases
HBAR serves multiple functions within the Hedera ecosystem:
- Transaction Fees: HBAR is used to pay for network services, including transferring HBAR, creating tokens, and executing smart contracts with low, predictable fees.
- Network Security: Through a proof-of-stake (PoS) model, users can stake HBAR to help secure the network. Hedera’s asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) ensures maximum security against malicious attacks.
- dApp Development: Developers leverage HBAR to deploy decentralized applications (dApps), execute smart contracts, and tokenize assets using the Hedera Token Service (HTS).
- NFT Creation: Hedera’s low transaction costs make it a perfect platform for minting and trading NFTs and digital collectibles.
⚙️ Hedera Hashgraph vs. Traditional Blockchain
Hedera stands out from traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum due to its:
- Lightning-Fast Transactions: Over 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), with finality in seconds.
- Eco-Friendly Operations: Poised as a carbon-negative network with minimal energy consumption per transaction.
- Low and Fixed Fees: Consistently low transaction fees (as low as $0.0001 per transaction).
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Achieving aBFT, the highest standard of security for distributed systems.
🌍 Enterprise Adoption and Real-World Use Cases
HBAR is rapidly gaining traction across multiple industries, from finance to supply chain management:
- Finance: Hedera is used for secure, fast payment processing and tokenization of financial assets.
- Gaming: High-speed, low-cost microtransactions are ideal for play-to-earn (P2E) gaming platforms.
- Healthcare: HBAR powers secure and immutable patient record management.
- Sustainability: Hedera supports green initiatives such as carbon credit tracking and transparent supply chains.
🌟 Who Governs Hedera? Meet the Hedera Governing Council
The Hedera network is governed by a council of up to 39 leading global companies, including tech giants like:
- Google Cloud
- IBM
- Boeing
- Deutsche Telekom
- LG Electronics
This decentralized governance model ensures long-term stability, continuous innovation, and enterprise-grade reliability.
💹 Is HBAR a Good Investment? Price Prediction and Market Outlook
As more enterprises adopt Hedera Hashgraph, the demand for HBAR is expected to grow. Analysts often highlight HBAR’s potential due to:
- Institutional Support: Backed by leading organizations through the governing council.
- Growing dApp Ecosystem: Increasing developer adoption for DeFi, NFTs, and enterprise use cases.
- Sustainability Focus: Ideal for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investors due to its green technology.
📈 Where to Buy HBAR Cryptocurrency
You can buy, sell, and trade HBAR on major cryptocurrency exchanges like:
- Binance
- Coinbase
- Kraken
- KuCoin
🚀 Future of HBAR and Hedera Hashgraph
The future of HBAR looks promising as Hedera continues to roll out updates such as:
- EVM-Compatible Smart Contracts 2.0: Bridging Hedera with the Ethereum ecosystem.
- DeFi Protocols and Liquidity Pools: Expanding Hedera’s decentralized finance offerings.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Enabling HBAR to be used across multiple blockchain networks.
📝 Conclusion: Why HBAR is More Than Just Another Cryptocurrency
Hedera Hashgraph and HBAR stand out as leaders in the blockchain space by combining speed, security, scalability, and sustainability. Whether you are a developer looking to build fast and secure dApps, an enterprise seeking robust blockchain solutions, or an investor exploring the next big cryptocurrency, HBAR offers unparalleled potential.
Find HBAR price data here.