ChainLink (LINK) Analysis
In addition to automated chart patterns, altFINS’ analysts conduct technical chart analyses of top 50 cryptocurrencies. We call these Curated Charts and they evaluate 5 core principals of technical analysis: Trend, Momentum, Patterns, Volume, Support and Resistance. Read technical analysis of ChainLink below.
Chainlink (LINK) Trends
Chainlink (LINK) Performance
Chainlink (LINK) RSI & MACD
ChainLink (LINK) technical analysis:
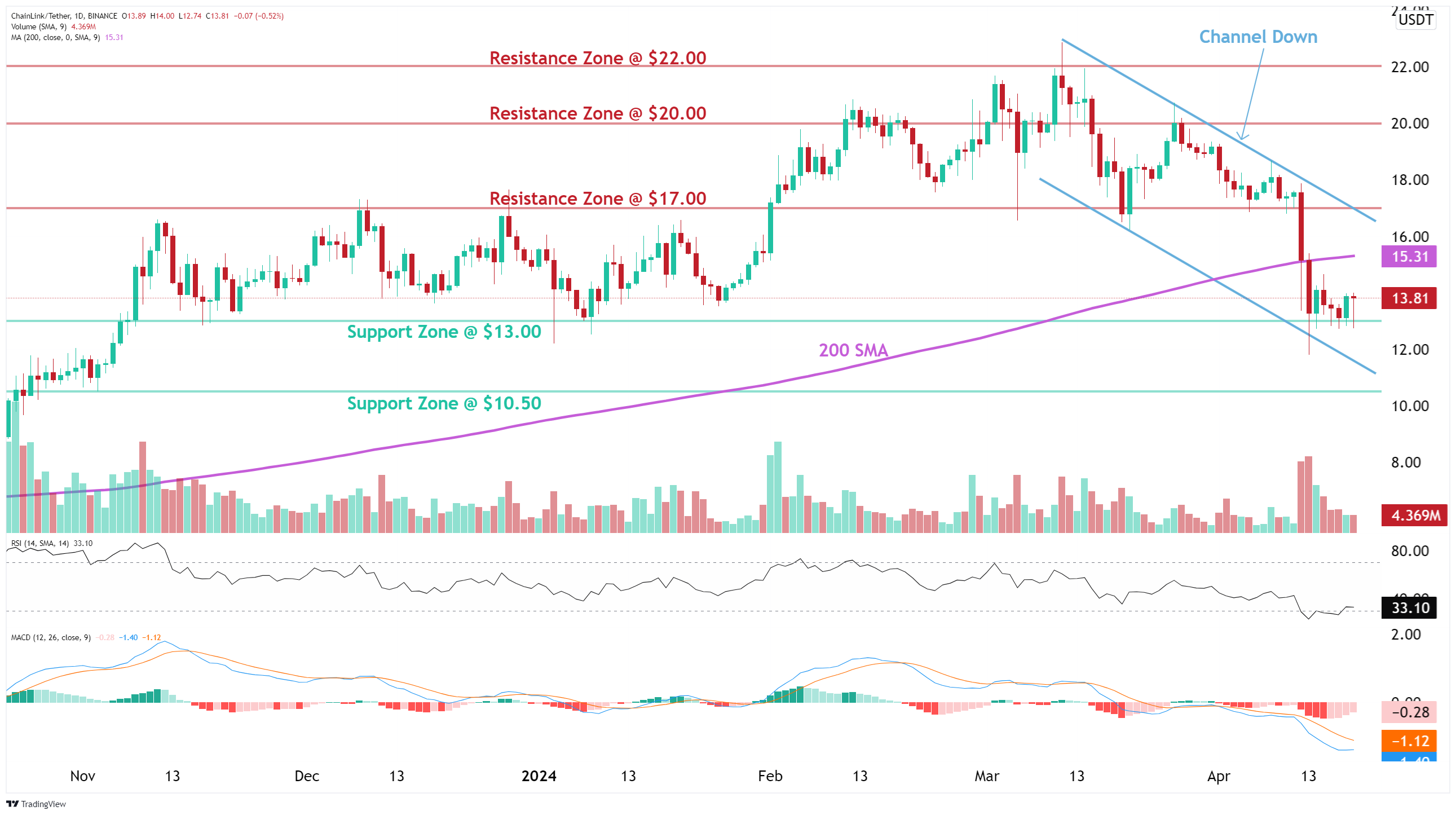
Trade setup: Trends are mixed. Price has broken below an important support level at $17 and below the 200-day moving average, which also puts the long-term trend at risk. Now it’s been sitting on $13 support level, which held up several times in late 2023 and early 2024. Price is also oversold (RSI < 30), which means it could bounce up near-term. Trend traders: wait for a breakout from Channel Down and above 200-day MA (~$15.30) to signal resumption of uptrend. (set a price alert). ChainLink (LINK) was our research Coin Pick and is up 100% since our initiation report (August 2023). As a leading oracle data provider, it should benefit from long-term trend in tokenization of real-world assets (RWA) like US T-Bills.
Trend: Downtrend on Short- and Medium-Term basis and Uptrend on Long-Term basis.
Momentum is Bearish but inflecting. MACD Line is below MACD Signal Line and RSI is below 45 but momentum may have bottomed since MACD Histogram bars are rising, which suggests that momentum could be nearing another upswing.
Support and Resistance: Nearest Support Zone is $13.00, then $10.50. The nearest Resistance Zone is $17.00, then $20.00 and $22.00.
See live ChainLink (LINK) chart here
See more curated charts of coins with technical analyses.
 Recent news and research:
Recent news and research:
Millions of LINK Acquired by Whales Since Chainlink Successful Swift Test
Chainlink Launches Staking Service as LINK Rallies 32%
Just In: Robinhood Lists Chainlink (LINK); Price Up By 5%
LINK spikes 24% following Chainlink reveal of ‘Economics 2.0’ roadmap
The Year in Chainlink 2021: 7 Pillars of Momentum
Institutions can now more easily access Aave (AAVE) and Chainlink (LINK)
Find more real-time news here.
What is ChainLink (LINK)?
Find full description and news on altFINS platform.
Overview of ChainLink
ChainLink is a decentralized oracle network. It seeks to operate as a middleman between smart contracts on smart contracting platforms and outside data sources, enabling smart contracts to safely access off-chain data feeds.
ChainLink History
In order to build a link between external data sources and open blockchains, ChainLink’s parent business SmartContract.com was established in September 2014. A product named ChainLink was ultimately created by the team, enabling smart contracts to connect to data feeds from any online API and data source. But because the initial SmartContract.com oracle solution for public blockchains relied on centralized oracles, it gave rise to the so-called “oracle dilemma”—a difficulty that results from smart contracts’ reliance on reliable outside sources of data. With the ChainLink network, a fresh decentralized oracle network, SmartContract.com made an effort to solve this issue in 2017.
To fund the project’s development, SmartContract.com (SmartContract ChainLink Ltd) raised $32 million through an initial coin offering. The ChainLink network aims to connect open blockchains and external data sources. Through its decentralized oracle network, it links smart contract platforms to crucial off-chain data from markets, events, and payments. Anyone with a data feed or other API can sign up for the Chainlink network and take on tasks to retrieve and distribute data to smart contracts. For their services, node operators are compensated in ChainLink tokens (LINK). When staking launches on the mainnet, node operators will also be able to stake LINK to fulfill specific smart contract demands that call for collateral. On June 1, 2019, Chainlink’s mainnet went online on Ethereum.
Technology of ChainLink
On-chain and off-chain components both exist in ChainLink. ChainLink is a network of oracle nodes that connects to open blockchains off-chain (initially just Ethereum). ChainLink on-chain is made up of a number of smart contracts that operate as an interface for contracts that want to request data feeds. A network of oracle nodes linked to the Ethereum blockchain makes up the off-chain portion of ChainLink. These nodes harvest off-chain answers on their own. A smart contract on Ethereum aggregates each participant’s individual responses, weights them, and then returns the results to the requesting contract. The standard open source core implementation, which manages typical blockchain interactions, scheduling, and connecting with external resources, powers ChainLink nodes.
The on-chain portion of ChainLink is made up of three major contracts: an aggregating contract, an order-matching contract, and a reputation contract. Oracle service provider performance indicators are tracked by the reputation contract. The order-matching smart contract takes proposed service level agreements (SLAs), which may include information such as query parameters (which data feeds to use), the quantity of oracles the buyer needs, collateral specifications, and uptime demands, and logs them. It also solicits quotes from oracle providers. The Oracle SLA is then finalized when bids are chosen utilizing the reputation contract. The ChainLink query’s final collective result is determined by the aggregating contract, which compiles the oracle providers’ responses. Additionally, the reputation contract receives metrics from the Oracle provider.
This process starts with a user smart contract. Data request parameters are defined by user smart contracts that publish contracts with SLAs. The order matching contract, which both collects bids and logs the SLA parameters, is used by node operators who watch the Ethereum blockchain for these requests to bid to service them. Through the ChainLink core team marketplace or other marketplaces for matching requests, users can even choose particular node operators by hand. Node operators who match a request node return external data to the aggregating contract, which combines the data into a single weighted value, transmits performance metrics to the reputation contract, and then reports the single weighted value back to the smart contract that requested it. Node operators are paid in LINK as payment for their services. Although all smart contract networks will eventually be integrated with LINK, it is currently based on the Ethereum platform.
About altFINS
altFINS is the best crypto analytics platform. The platform will help you find the right crypto trading opportunities. You can search for coin in Uptrend, with Momentum or Breakouts. It’s is great for advanced traders but also for beginners to learn basics of technical analysis in Crypto trading Course or in Curated charts or Chart pattern sections. But also more advanced traders can create their own Screens and Alerts of coins with different trading strategies.
