ICP (ICP) Analysis
The Internet Computer (ICP) Analysis
In addition to automated chart patterns, altFINS’ analysts conduct technical chart analyses of top 30 cryptocurrencies. We call these Curated Charts and they evaluate 5 core principals of technical analysis: Trend, Momentum, Patterns, Volume, Support and Resistance.
The Internet Computer (ICP) technical analysis:
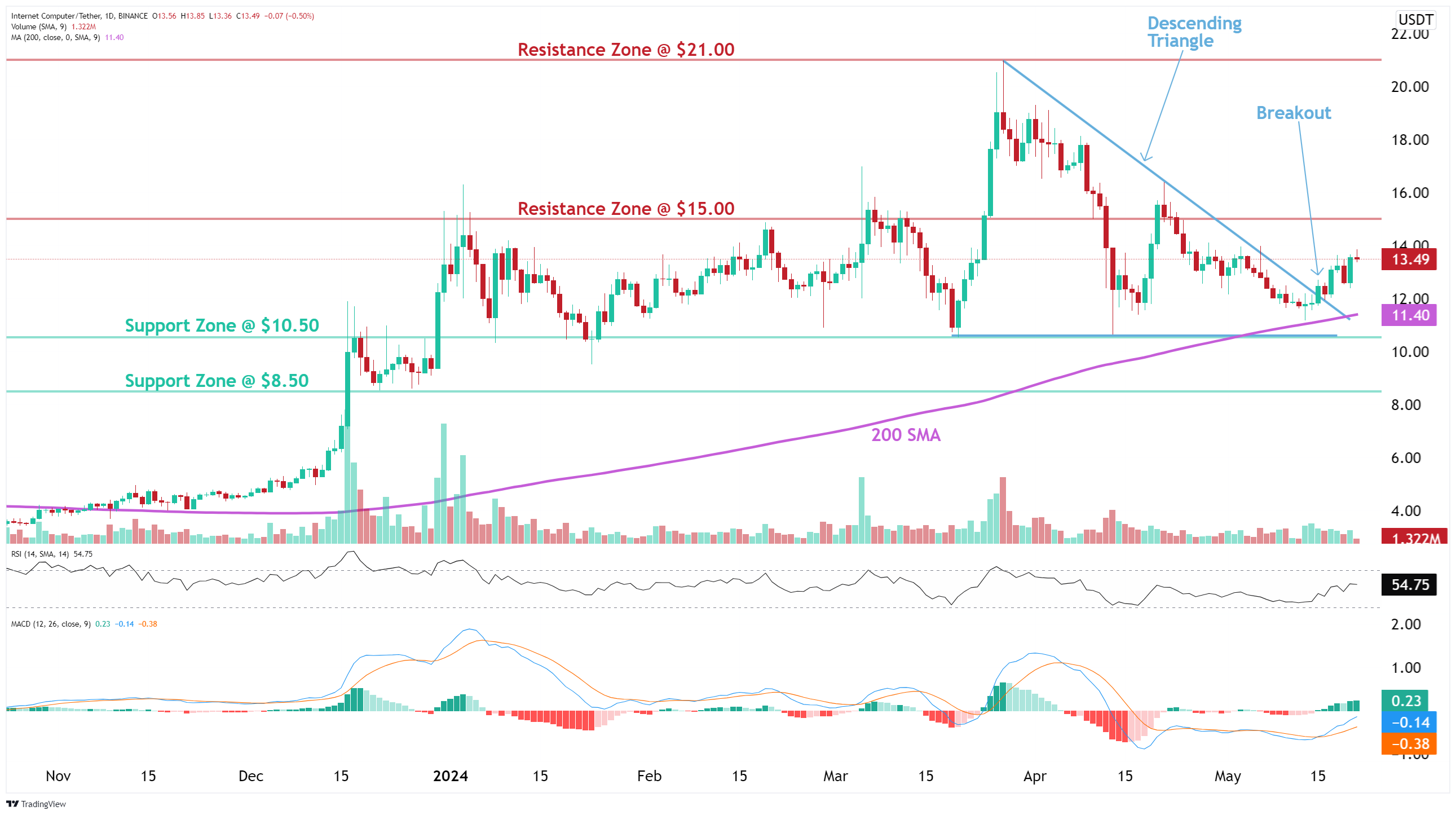
Trade setup: Trends are mixed. Price bounced off of 200-day moving average (~$11.20) and broke out of a Descending Triangle pattern. Price could revisit $15.00 near-term. Stop Loss (SL) level at $10.30. Learn to trade key level breakouts in Lesson 7. (set a price alert).
Trend: Uptrend on Short-Term basis, Downtrend on Medium-Term basis and Neutral on Long-Term basis.
Momentum is Mixed as MACD Line is above MACD Signal Line (Bullish) but RSI ~ 50 (Neutral).
Support and Resistance: Nearest Support Zone is $10.50, then $8.50. The nearest Resistance Zone is $15.00, then $21.00.
See live The Internet Computer (ICP) chart here
See more curated charts of coins with technical analyses.
Recent news and research:
Highlights June 3: Cryptos mixed, ICP rises after Binance delists futures pair
Find more real-time news here.
What is The Internet Computer (ICP)?
Find full description and news on altFINS platform.
Overview
The Internet Computer (IC) is a blockchain network built by the DFINITY Foundation that aims to support smart contract development at scale. It’s an attempt to reinvent how users interact with internet applications as its nodes run on specialized hardware housed by various independent data centers. The IC lets developers deploy and run applications through the use of canisters, which are akin to smart contracts. Each canister has a storage capacity of 4GB. The IC features two core tokens: ICP is the network’s governance token, and Cycles (created by burning ICP) are a form of stablecoin that allows users to pay for computational resources and network transactions.
History
The Internet Computer (IC) is a blockchain network built by the DFINITY Foundation that aims to run decentralized applications at web speed. It’s an attempt to reinvent how users interact with internet applications as its nodes run on specialized hardware housed by various independent data centers. The IC lets developers deploy and run applications through the use of canisters, which are akin to smart contracts. Each canister has a storage capacity of 4GB. DFINITY’s vision is for its new internet infrastructure to support a wide variety of end-user and enterprise applications, such as social media, messaging, and data storage. The project was founded as DFINITY in October 2016 by Dominic Williams. DFINITY raised a total of $121 million from contributors such as Andreessen Horowitz, Polychain Capital, SV Angel, Aspect Ventures, Electric Capital, ZeroEx, Scalar Capital, and Multicoin Capital. In 2018, the DFINITY Foundation distributed ICP tokens to 50,000+ registered participants through an airdrop. On December 18, 2020, DFINITY launched the alpha mainnet of the Internet Computer. The team then launched the Internet Computer into the public domain on May 10, 2021. Its public launch also marked the release of the Internet Computer’s source code and the ICP utility token’s transaction and governance functionalities.
Technology
The purpose of the Internet Computer (IC) is to extend the public internet. The current internet is a network that connects everybody and everything, but systems and services run on infrastructure managed by private companies. The IC aims to upend this model through the creation of Chain Key Technology, which includes several complementary components like a new consensus model (Threshold Relay), Non-Interactive Distributed Key Generation (NI-DKG), an on-chain governance system (the Network Nervous System or NNS), and decentralized identity (Internet Identity). Chain Key Technology consists of a set of cryptographic protocols that orchestrate the nodes that make up the Internet Computer. It enables the IC to have a single public key, which is small enough (in size) to allow any device, like smartwatches and mobile phones, to verify the authenticity of artifacts from the Internet Computer. Chain Key Technology is the engine that drives the Internet Computer and makes its operation possible. It allows for: Adding new nodes to form new subnets to help scale the network Replacing faulty or crashed nodes with new ones without stopping Reviving subnets even if too many nodes within have failed Upgrading the Internet Computer Protocol, allowing the network to fix bugs and add new features The DFINITY R&D team has also invented a new noninteractive key resharing protocol. Each of the old signers only needs to broadcast a single message to the new signers. To ensure that this is done securely, many concepts from advanced cryptography are utilized, including encryption with forward secrecy and noninteractive zero-knowledge proofs. Because it is noninteractive, the way the key resharing protocol operates is ideal for an asynchronous environment, and the benefits include key preservation. Throughout the lifetime of a subnet, it is known by a single public key, and the other parties on the Internet Computer do not have to keep track of changing public keys.
Usage Details
ICP is the Internet Computer’s native utility token. It plays three key roles in the network: Facilitating Network Governance: ICP tokens can be locked to create neurons that participate in network governance by voting, through which they can earn economic rewards. Production of Cycles for Compute: ICP can be converted into “cycles,” which power computation in the role of fuel that is burned when it is used. The Network Nervous System (NNS) governance mechanism converts ICP to cycles at a variable rate. This rate is chosen to ensure users of the network can always create new cycles at an approximately constant cost in real terms, such that the cost of acquiring fuel is predictable. Participant Rewards: The network mints new ICP to reward and incentivize those contributing to the network and enabling it to function. These contributions include (1) the provision of “voting rewards” to those participating in governance, (2) the provision of “compute rewards” to those operating the node machines hosting the network, and (3) other miscellaneous activities.
Asset profile is provided by messari. Original version can be found at Messari