Bitcoin (BTC) Analysis
Bitcoin (BTC) Analysis
In addition to automated chart patterns, altFINS’ analysts conduct technical chart analyses of top 30 cryptocurrencies. We call these Curated Charts and they evaluate 5 core principals of technical analysis: Trend, Momentum, Patterns, Volume, Support and Resistance.
Bitcoin (BTC) technical analysis:
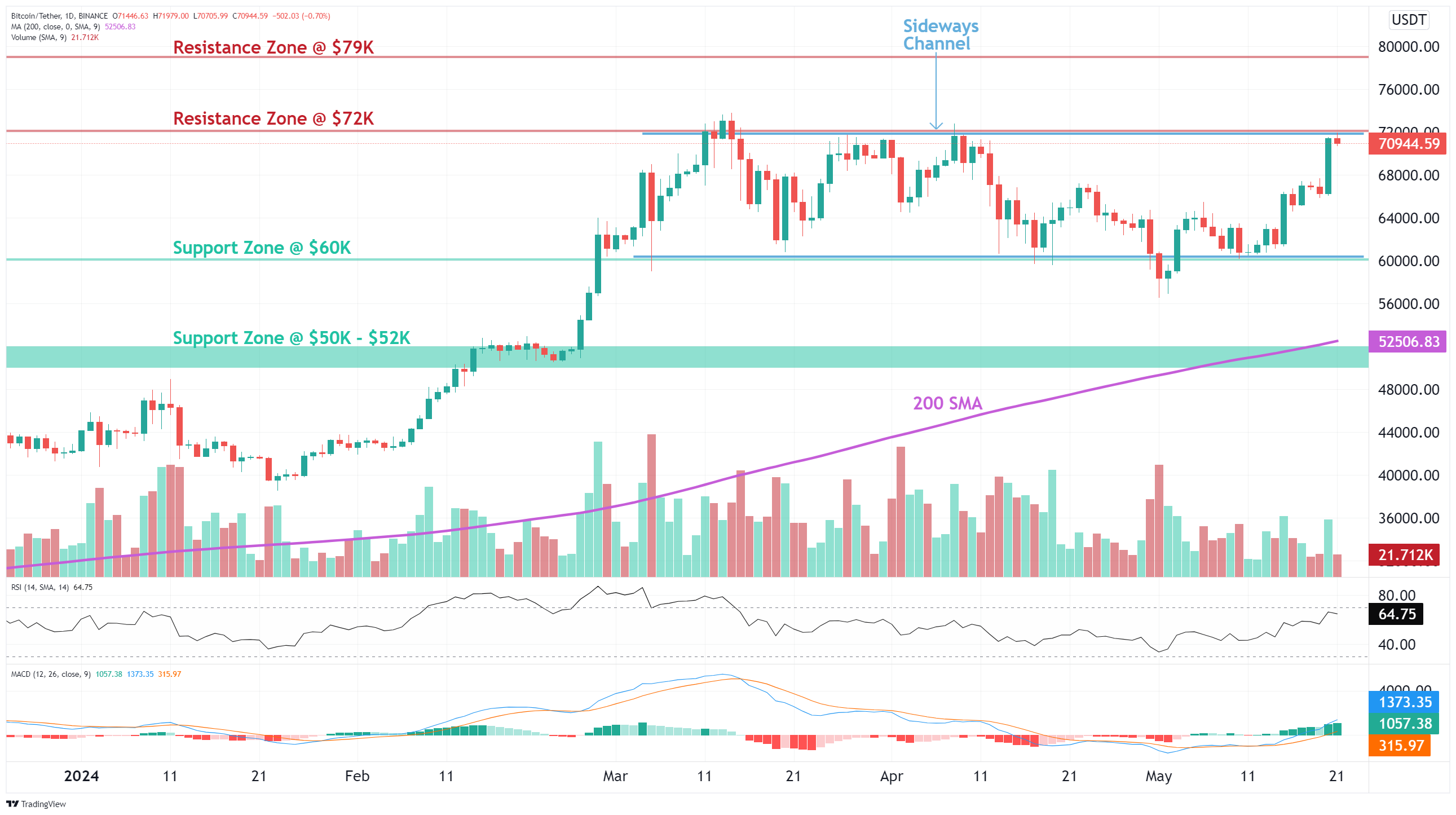
Trade setup: Price is in an Uptrend, consolidating in a Sideways Channel. It briefly broke below a key level of $60K but recovered back above it and successfully retested that $60K level. Now it’s approaching $72K-$74K resistance zone. If it breaks above that, price could head to $79K next. Swing traders: could trade the channel – enter near $60K and exit near $72K. Stop Loss at $55,800, just below prior swing low. (set a price alert).
Pattern: Price is trading in a Sideways Channel , which is a neutral pattern (indication of market indecision). Trend Traders ought to wait for a breakout in either direction. Learn to trade Sideways Channel in Lesson 6.
Trend: Uptrend across all time horizons (Short- Medium- and Long-Term).
Momentum is Bullish ( MACD Line is above MACD Signal Line and RSI is above 55).
Support and Resistance: Nearest Support Zone is $60K, then $50K. The nearest Resistance Zone is $72K, then $79K.
See live Bitcoin (BTC) chart here
See more curated charts of coins with technical analyses.
Recent news and research:
One man’s plan to orange pill a nation: Bitcoin Senegal
4 things to do before you invest a single dollar in bitcoin, according to a financial planner
Billionaire who shorted 2008 crisis has a bleak warning for Bitcoin (BTC)
US: A historic gold investor is now buying Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin Shows Signs of Exhaustion as Rally ‘Falters’ Before Next Leg Up: Sources
New York’s Leading Investment Manager Enters Cryptocurrency Market
Find more real-time news here.
What is Bitcoin (BTC)?
Find full description and news on altFINS platform.
Overview
Bitcoin is the first distributed consensus-based, censorship-resistant, permissionless, peer-to-peer payment settlement network with a provably scarce, programmable, native currency. Bitcoin (BTC), the native asset of the Bitcoin blockchain, is the world’s first digital currency without a central bank or administrator. The network is an emergent decentralized monetary institution that exists through the interplay between full nodes, miners, and developers. It is set by a social contract that is created and opted into by the users of the network and hardened through game theory and cryptography. BTC is the first, oldest, and largest cryptocurrency in the world.
History
Pre-history Bitcoin borrows from nearly three decades of research by academics, cypherpunk practitioners, and hobbyists who tried to create similar payment protocols. Some of the most prominent projects that preceded it include: Digicash, b-money, Hashcash, e-gold, and Bit Gold. Bitcoin is often associated with Austrian economic theories, anarcho-capitalist principles, and general libertarian politicking by virtue of the exclusive developer community to whom Nakamoto first released their white paper, certain protocol design characteristics, and the political affiliations of early investors. Conception to Launch On October 31, 2008, at the peak of the Global Financial Crisis, just six weeks after the infamous investment bank, Lehman Brothers, declared bankruptcy, the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto released the Bitcoin whitepaper to the cryptography mailing list. Titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, the whitepaper proposed a new electronic cash system that would allow fully peer-to-peer online payments without reliance on trusted third parties. Soon after the release of the whitepaper, Satoshi implemented the software as open-source code. On 3 January 2009, the Bitcoin network came into existence with Satoshi mining the genesis block of Bitcoin, which included a now-famous “The Times” headline in the coinbase both to prove the network’s fair launch and to make a political statement about the global financial system.
The event marked the birth of the world’s first non-sovereign, decentralized, digital money. Post Launch Hal Finney, who invented the first reusable proof-of-work system (RPoW) in 2004, received the first transaction (10 bitcoins) on January 12, 2009. In 2010, the first known commercial transaction using bitcoin occurred when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John’s pizzas for 10,000 bitcoins.
In August 2010, a major vulnerability in the protocol was spotted and exploited in the network, allowing users to create an infinite amount of bitcoins. The transactions exploiting the vulnerability were quickly spotted and erased for the Bitcoin blockchain, with the vulnerability being patched in a network upgrade of the protocol. This was the only major security flaw found and exploited in its history.
In December 2010, amidst rising publicity from Bitcoin’s use in financing Wikileaks, Satoshi Nakamoto, disappeared from involvement with Bitcoin. It is unknown why Satoshi disappeared from the project, although some believe Satoshi, cognizant of past struggles to launch a digital currency, recognized that a leader of the project could be a central point of failure. It is estimated that Nakamoto had mined about one million bitcoins before disappearing in 2010 when he handed the network alert key and control of the code repository over to Gavin Andresen.
Silk Road & Mt. Gox. One of the most iconic early use cases for Bitcoin was the Silk Road. Launched in early 2011, the Silk Road was a darknet marketplace that allowed users to buy and sell a wide variety of goods including, most notably, illegal drugs. Underpinning the Silk Road was the Tor network, which allowed users to browse the Silk Road anonymously and securely without potential traffic monitoring, and Bitcoin which provided a censorship-resistant payment rail for pseudonymous transactions. Over the course of its life, it is estimated that the Silk Road facilitated more than $1.2 billion in transactions, collecting over $80 million in sales commissions, leveraging the network as its payment rail. The site was shut down in 2013 when the FBI took advantage of the Silk Road’s centralized infrastructure, arresting founder Ross Ulbricht, and shuttering the site.
Founded by Jed McCaleb in July 2010, and led by Mark Karpeles until it collapsed, Mt. Gox was one of the earliest exchanges in the world. Based in Tokyo, Japan, the exchange would go on to handle over 70% of all bitcoin (BTC) transactions worldwide at its peak. Known for its chronic security issues, Mt. Gox was infamously hacked in 2014, losing 850,000 bitcoins worth about $450 million at the time. The hack sent the price of Bitcoin, which was in the midst of one of its first major price bubbles, plummeting. Bitcoin would sink into a bear market with prices not recovering until the 2017 bull run. 2017 Bubble & Bitcoin Cash Hard Fork The 2017 price bubble was a watershed moment for Bitcoin. The price of Bitcoin rose more than 1900% from just under $1,000 at the beginning of the year to near $20,000 at its peak in December. At its peak, Bitcoin’s market capitalization eclipsed $325 billion. Along with the proliferation of Initial Coin Offerings, powered by Ethereum, Bitcoin’s incredible 2017 run propelled cryptocurrency into mainstream consciousness, among the most discussed phenomena of 2017. Also notable in 2017, Bitcoin experienced its most contentious fork to date. Amidst rising transaction fees on Bitcoin and increasingly divergent views on scaling Bitcoin, an agreement was reached amongst prominent Bitcoin stakeholders in what is now known as the “New York Agreement”. The agreement was to support a set of network upgrades called SegWit2x. The proposal was backed by over 80% of Bitcoin’s hash rate. However, despite the desires of miners, users wanted to activate SegWit without the 2MB block size increase, the philosophy underpinning this decision being that the users controlled the network, not miners and Bitcoin businesses. Subsequently, they set a date (August 1, 2017) where Bitcoin would soft fork to support SegWit and keep the 1MB block size. Enough nodes signaled support for it that they forced miners to accept or have their blocks rejected by the network. A faction of the bigger blocks camp, rejected SegWit altogether, citing frustrations with the prioritization of SegWit over bigger blocks, and on August 1, 2017, they launched a hard fork of Bitcoin called Bitcoin Cash, with 8MB block limits. These events marked, one end, a landmark demonstration of power by the users of the Bitcoin network, and on the other end, the first great schism within the Bitcoin community. 2018 – 2019 After peaking in December 2017, Bitcoin, along with the rest of the cryptocurrency market in January 2018, crashed, sending the cryptocurrency market into its latest bear market. Since then Bitcoin has dropped as low as $3,200, more than 80% below its ATH. However, while prices have yet to recover to 2017 highs, the institutionalization of Bitcoin has picked up significantly. Traditional Wall Street institutions including Chicago Mercantile Exchange, Intercontinental Exchange, and Fidelity have all launched cryptocurrency offerings, opening up the market to institutional investors. There are now several regulated exchanges and custodians. Furthermore, regulatory clarity around Bitcoin has improved dramatically with SEC Chairman, Jay Clayton, revealing at a Congressional hearing in February 2018, that the SEC does not consider Bitcoin to be a security. Since it reached its cycle low in February 2019, Bitcoin’s price has recovered considerably, rising as high as $13,000 in June. With the recent announcements of Facebook’s Libra project and China’s Central Bank digital currency, governments and multinational corporations around the world have begun to look at cryptocurrencies more seriously. American officials are debating a digital dollar and lawmakers around the world are considering the central bank digital currency (CBDC) options. Furthermore, there have been numerous cryptocurrency-related hearings since Libra was announced. China has recently announced blockchain was a revolutionary technology and that it would make blockchain technology a strategic imperative for the country. Bitcoin’s price rose more than 40% after the announcement, its highest intraday movement since 2011. 2020 – 2021 Bitcoin traded sideways into 2020, but the onset of the novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic saw world markets take the biggest dips since at least the 2007-08 Mortgage Crisis. Bitcoin did not escape the dip – in less than 48 hours it lost half of its value, going below $4,000 for the first time since March of 2019. Luckily for bitcoiners, bitcoin rebounded, returning to its pre-pandemic price in less than a month. Bitcoin’s ascent recovery out of the March turmoil drew wider media and institutional attention and lent credibility to its store of value narrative. Although it remained around $10,000 throughout Ethereum’s firey DeFi summer, bitcoin would start to trend upwards into the fall and by early November bitcoin hit $14,000. Whether it was unprecedented levels of money printing by the Federal Reserve, its V-shaped recovery in April, or direct stimulus payments to millions of Americans, it was clear bitcoin wasn’t done at $14,000 as it crossed $20,000 for the first time ever on December 16, 2020. Two weeks later it hit $28,000. Then, on January 8, 2021, bitcoin set a new all-time high of $41,429.38. Since hitting $41,000 bitcoin has mostly drifted in the $30,000. Bitcoin’s price wasn’t the only thing rapidly accelerating in 2020. Institutional adoption skyrocketed. Led by Paul Tudor Jones of Microstrategy ( $1 billion), institutions joined the bitcoin world en masse. From insurance companies like MassMutual ($100 million) to investment firms like Ruffer ($744 million) new groups continue to adopt bitcoin. And institutions aren’t alone – entrepreneurs like Elon Musk and politicians like Miami Mayor Francis Suarez have increasingly promoted bitcoin. Even athletes have joined the space, as NFL player Russell Okung partnered with Bitcoin Lightning Company Zap to become the first professional sports player ever to be paid in bitcoin.
Supply Curve Details
Bitcoin Halving Schedule. The rate at which new bitcoins are created is algorithmically cut in half roughly every 4 years (210,000 blocks). Bitcoin has gone through three halvings to date; November 2012, July 2016 and most recently in May 2020. Since blocks are generated every 10 minutes on average and starting at 50 new bitcoins per block when the system was launched in 2009, this creates a very well-defined supply curve.
The stability of Bitcoin’s monetary policy. Bitcoin’s monetary policy is disinflationary. The annual rate of inflation decreases through time. The current supply cap is set at 21 million coins. The stability of monetary policy provided by this well-defined supply cap and halving schedule is a key differentiator versus other crypto assets.
Consensus Details
Consensus Bitcoin pioneered and currently uses Nakamoto Consensus whereby the valid chain is the longest chain with the most accumulated proof-of-work. Consensus in Bitcoin, and other systems using Nakamoto Consensus, is probabilistic because there is always a chance that a new, longer competing chain could emerge with more accumulated proof-of-work, that would invalidate the current chain. Learn More: How Does Distributed Consensus Work Anyways? Nakamoto Consensus Mining Miners solve computational puzzles to generate new blocks using a SHA-256 algorithm. In this process, miners compete to generate a hash less than the target number set by Bitcoin’s difficulty adjustment algorithm. The target difficulty level is adjusted every 2016 blocks. Although open to anyone with a CPU, mining is now dominated by ASICs situated in enterprise-scale data centers. In order to smooth individual miner revenue as mining has become more competitive, mining is now done in pools where participants contribute hash power to the pool and receive a proportional share of the profits if the pool finds a valid block. Learn More: Cryptocurrency Mining State of Cryptocurrency Mining.
Usage Details
BTC is used as a native currency within the Bitcoin network. BTC can be used for peer-to-peer payments and value storage within the network. It is also used to pay fees for transactions. In efforts to keep it decentralized, with its small, limited block sizes and low on-chain throughput, it leverages off-chain payment channels for increased scalability. It is in this respect that it acts as a payments settlement network. Throughout its life, Bitcoin has most notably served as a digital currency for online marketplaces, a settlement layer for transferring value between Bitcoin exchanges, a capital-raising mechanism for novel cryptocurrency projects, a collateral asset for lending products, and a speculative store of value.
Launch Details
Satoshi Nakamoto created the first bitcoins on January 3, 2009, by mining the genesis block. The genesis block mining reward (50 BTC) is unspendable due to the original client’s block database and transaction database configuration. The coinbase of the first block included the following text: “The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks” This text has been interpreted both as a proof that the block was created on January 3, 2009, as well as a comment on fractional-reserve banking. Hal Finney received the first bitcoin transaction on January 12, 2009. Finney had downloaded the bitcoin software when it was first released and was known the be the creator of RPoW, the first reusable proof-of-work system, in 2004.
Asset profile is provided by messari. Original version can be found at Messari